INSTITUTION OF AGROFORESTRY FARMERS AND TECHNOLOGISTS
Menu
IAFT – INSTITUTION OF AGROFORESTRY FARMERS AND TECHNOLOGISTS
Botanical Name | Casuarina equisetifolia L. |
Name in English | Casuarina |
Name in Kannada | Sarve Mara |
Family | Casuarinaceae |
Seeds Collection | Casuarina seeds are small consisting 5 to 6 lakh seeds per kg. |
Seeds Processing & Treatment | Generally, no pre-treatment is necessary for Casuarina seeds |
Nursery | Germination is generally around 30% and about 30,000 to 100,000 seedlings are obtained from a kg of seed depending upon source of seed and nursery efficiency. Seeds are sown in raised sand beds (called ‘mother beds’) of the size 10 x 1 m. In each bed about 250 g of seeds are evenly spread by mixing with fine sand. They are overlaid with a thin layer of sand. The sand bed is covered with rice straw to prevent washing off of seedlings while watering. Water is provided through a rose can or a sprayer. A suitable repellent is applied along the periphery of the bed to prevent ants removing the seeds. Seeds start germinating from the 5th day and the straw is removed on the 7th day. They are grown in the mother beds for the next 3 to 4 weeks. After 4 weeks when the seedlings attain 8 – 10 cm height they are transferred either to a secondary bed or polythene bags. Secondary beds are also of the same size as the mother beds but in addition to sand, farm manure and soil (2:1:1) are also added to increase nutrient availability and water holding capacity. Seedlings |
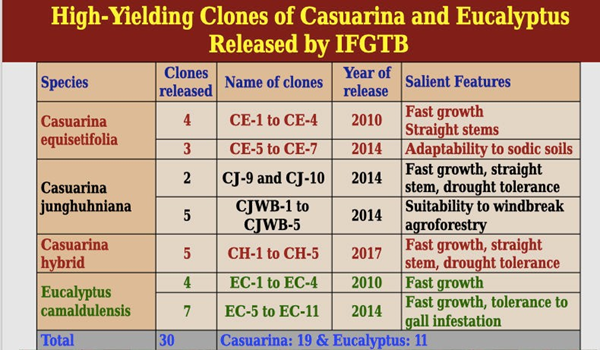
pricked from the primary beds are transplanted in the secondary bed at approximately 4 cm apart. Seedlings are grown in the secondary beds for 3 months to obtain a height of 30 to 45 cm and a collar diameter of 3 to 5 mm. Growing seedlings in polybags and root trainers is better than bare root seedlings especially for planting in rain fed areas. Seedlings raised in containers establish well in plantations and record vigorous growth in the first year. Polybags (size: 15 x 7 cm) filled with a potting mixture of sand, farm manure and soil in a ratio of 2:1:1 are suitable for raising Casuarina seedlings. Seedlings may attain plant able size within 2 months but can be maintained for another 4 to 6 months if planting is delayed. Further farmers can try out new high yielding casuarina variants namely IFGTB- CH 1 to 5, developed by IFGTB Coimbatore. | |
Plantation Management | Since casuarina is planted as bare-root seedlings, planting them just before or during the rains ensures high survival especially under rainfed conditions. Where irrigation is available, it is recommended to plant one month before the rain and provide water once or twice a week. This will help the plants to establish well before the arrival of monsoon and grow faster than those planted during the rain. Land must be preferably disc ploughed twice. Pit size for planting container-raised plants (poly bag or root trainer) is 30 cm x 30 cm x 30 cm. The recommended spacing for realizing full potential of genetically improved planting stock is 1.5 x 1.5 m. Add a basal dose of 10 g of super phosphate per pit before field planting of seedlings. Application of anti-termite solution (e.g. chlorophyriphos 1ml per litre of water) may be needed in red soils or where the problem has been encountered before. This may not be necessary in sandy soils in coastal areas. If no rain received immediately after field planting of seedlings, watering in alternate days is necessary for the first two weeks. The frequency may be reduced gradually to once or twice a week depending upon local conditions. Casualty replacement should be taken up only up to one month after planting. Four weedings needs to be carried out at 3, 6, 9 and 12 months or till the canopy closes whichever is later. Two prunings need to be taken up at 12 and 24 months. Fertilizer application is not necessary after planting if the land is fairly fertile. In low-nutrient soils DAP 100 kg per acre may be applied between 12 and 24 months. |
Fertilizer application is generally restricted to irrigated plantations and varies between regions and even among farmers. Fertilizers will have the maximum effect if applied during the peak growing period of 12 to 24 months. Farmers generally apply 50 kg of urea and 50 to 100 kg of DAP per acre one year after planting. Casuarina does not need large quantity of nitrogen fertilizer since it produces its own nitrogen with the help of the bacterium, Frankia. So it is recommended to apply 11 kg of urea and 94 kg of super phosphate at four stages: immediately after establishment, 6, 12 and 18 months after planting. Pruning of side branches is usually carried out between first and second years and second and third years. The expenditure for pruning is met by the sale of pruned material. It is also a common practice to intercrop groundnut, water melon or pulse crops in the first year well before the tree crown starts closing in and cause shade effect to agriculture crop. The plantation establishment cost is generally recovered from the agriculture crop. It also helps to keep the field weed- free | |
Model/Spacing | 1.8 x 1.8, 2 x 2 m or 2.4 x 2.4 m spacing is ideal. |
Pests, diseases and Management | Casuarina has only a few major insect and disease incidence which can lead to economic loss. The common insect problem in casuarina plantation is attack by the stem borer, Indarbela quadrinotata. The larvae dig up deep tunnels on the main stem and remain inside the tunnel during day time and emerge out in night and feed on the bark. Although the trees generally survive, the pole quality is affected by severe infection. Affected trees are also prone to breaking at the point of infestation during heavy wind. Chemical control of this insect is difficult since it resides within the tunnel. Insect attack can be prevented by planting varieties that are unaffected by the insect (e.g. Australia and Kenya). Wilt or blister bark disease caused by Trichosporium vesciculosum results in drying up of trees followed by large scale death. Affected trees show symptoms of drying of leaves followed by ‘blisters” on the main stem. At advanced stages these blisters burst open releasing black spores. The disease is not considered as a serious problem in plantations because it usually occurs in plantations older than 4 years age. There is no effective control measure once the infection occurred but removing and burning the infected tree can prevent |
further spreading of the disease. Australian, Kenyan and Malaysian provenances were found to be resistant to blister bark disease. | |
Plant Rotation | The commonly followed rotation period is 4 years with irrigation and 6 years under rain fed conditions. But the duration varies greatly in different areas and between farmers. In a few places of coastal Tamil Nadu irrigated casuarina is harvested as early as 2.5 years of age whereas Forest Department plantations without irrigation are retained up to 8 years. |
Yield | Wood production varies greatly across locations, cultivation techniques adopted and age at which harvested. Plantations with irrigation and fertilizer application yield 100 to 150 tonnes of air-dried wood (up to 20 cm girth) per hectare (40 to 60 tonnes per acre) in 4 years. Under rainfed conditions an average yield of 75 to 100 tonnes per hectare is obtained in 6 years (30 to 40 tonnes per acre) depending upon soil quality and amount of rainfall during the cultivation period. IFGTB supplies high quality seeds from seed orchards which can improve yield up to 25% and the superior clones (IFGTB CE 1, CE2, CE3, CE4, CJ9 and CJ10) produce up to 50% more yield |
Uses | Used for poles, cantering materials, fuel wood, Charcoal |
Buyers /Industries | In construction industry for use as scaffolding & poles and wood for roofing/ in furniture making, fencing posts, |
Harvesting | Harvesting starts from 7 years and continue up to 20years, if they followed coppice method. |
Economic Returns | Rs. 15,000 – 44,000 per ha per year |
Current Market Rate | Rs. 220 – 250 per tonne |